- admin
- February 27, 2025
Unearned Revenue Is Reported In The Financial Statements As

This accounting method recognizes revenue only when it is earned, not when the cash is received. It ensures that financial statements present an accurate view of the company’s financial health. As investors seek to make informed investment decisions, analyzing a company’s unearned revenue can offer an essential piece of the puzzle in evaluating its overall financial standing.
Reporting on the Balance Sheet
- This liability is a direct claim on future resources or services, making it a short-term obligation.
- CFI is on a mission to enable anyone to be a great financial analyst and have a great career path.
- In this case, companies don’t need to recognize unearned revenue or liabilities on their income statement, as all transactions are recorded when the cash is exchanged.
- It reflects a company’s future obligations and helps assess financial stability.
- By accurately accounting for these revenues, businesses can smooth out their income over time, enhance their budgeting processes, and make more informed decisions regarding investments and expenses.
- Unearned revenue, also known as advance payments, refers to a company receiving payment from a customer for goods or services that still need to be provided.
Companies ought to be meticulous in applying these norms, ensuring the systematic recognition of revenue as performance obligations are fulfilled. Discrepancies in the cash receipts may lead to issues with your statements of earning, credit rating, and (for publicly traded companies) stock impacts. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) closely monitors reporting to ensure investors have correct information on which to base their decision. BBCIncorp provides tailored support https://www.fida-cameroon.org/goods-received-note-full-form-of-grn-importance-4/ for offshore accounting, auditing and tax filing.
Company
Common examples of transactions resulting in deferred revenue include subscription-based services, prepayments for goods or services, advance ticket sales, and annual maintenance contracts. For instance, when a customer pays for a one-year magazine subscription, the publisher records the payment as deferred revenue and gradually recognizes it as income over the subscription period. Consider a company that publishes a monthly magazine and collects its yearly subscription fees upfront. The amount received for the entire year constitutes deferred revenue, and the online bookkeeping company recognizes it as a liability. As each month progresses and magazines are delivered, the company can recognize a portion of this payment as earned revenue. Unearned revenue is subject to strict accounting standards under GAAP and IFRS.
Mastering Unearned Revenue: Essential Accounting Practices for Advance Customer Payments

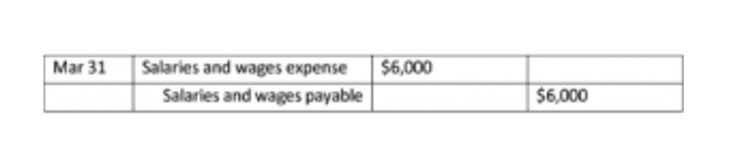
Knowing whether unearned revenue is a debit or credit ensures transactions are recorded correctly and that liabilities reflect the company’s pending obligations. Only after the unearned revenue is reported in the financial statements as company fulfills its obligations will the revenue be recognized on the income statement. This avoids overstatement of income and ensures accurate timing of revenue recognition.

Regulatory Bodies and Standards
- This means that the cash isn’t received in the current period, but it’s expected to be received in later periods as services are provided or products are delivered.
- This liability remains until the customer redeems the card for goods or services.
- Accounting for unearned revenue is inherently unique because even though it’s money in the bank, it’s not yet your earnings.
- The adjusting entry will always depend upon the method used when the initial entry was made.
- Understanding the benefits of unearned revenue is crucial for investors seeking to make informed decisions and businesses looking to optimize their financial performance.
- For instance, a software company receiving advance payments for a yearly subscription must allocate resources efficiently to maintain service quality over the subscription period.
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) uses the term “contract liability” in its Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 606, which governs revenue recognition. From the viewpoint of a CFO, unearned revenue is a financial instrument that can be used to stabilize cash flow and fund immediate operational needs. However, it requires meticulous forecasting to ensure that the company doesn’t overextend itself. For instance, a software company receiving advance payments for a yearly subscription must allocate resources efficiently to maintain service quality over the subscription period. This careful approach to accounting for unearned revenue can also offer valuable insights into a company’s cash flow management and operational efficiency.

